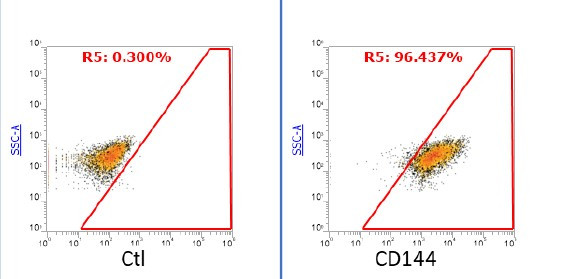
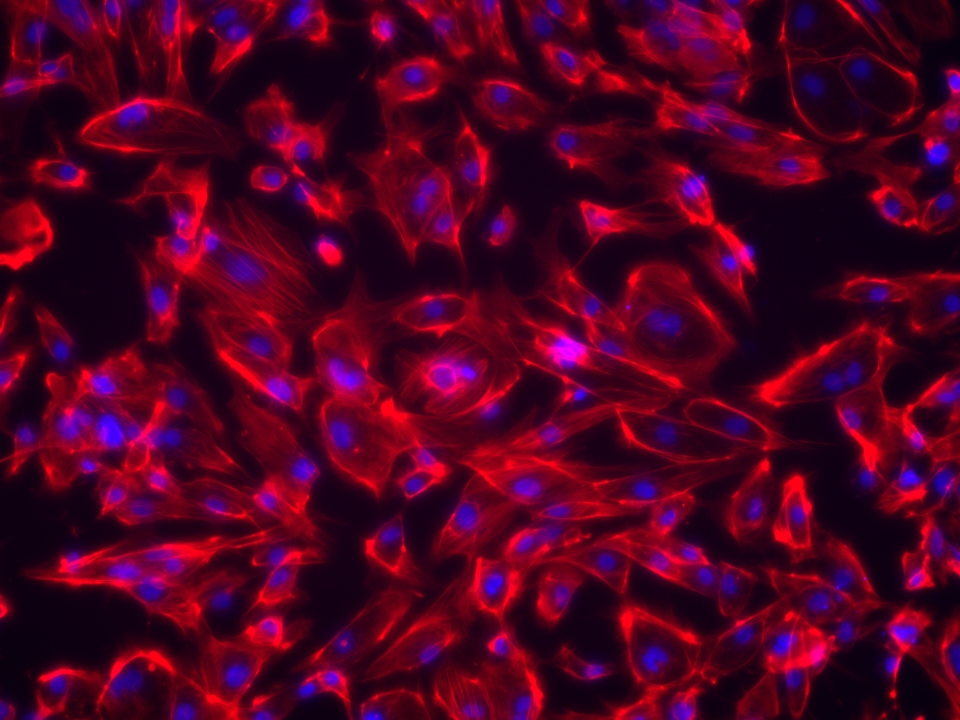
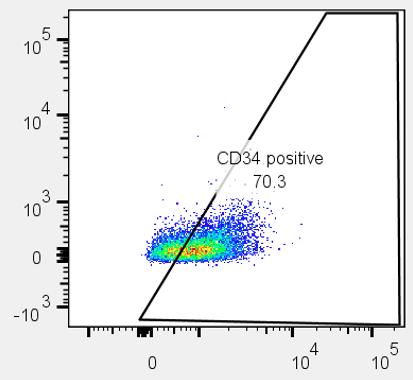
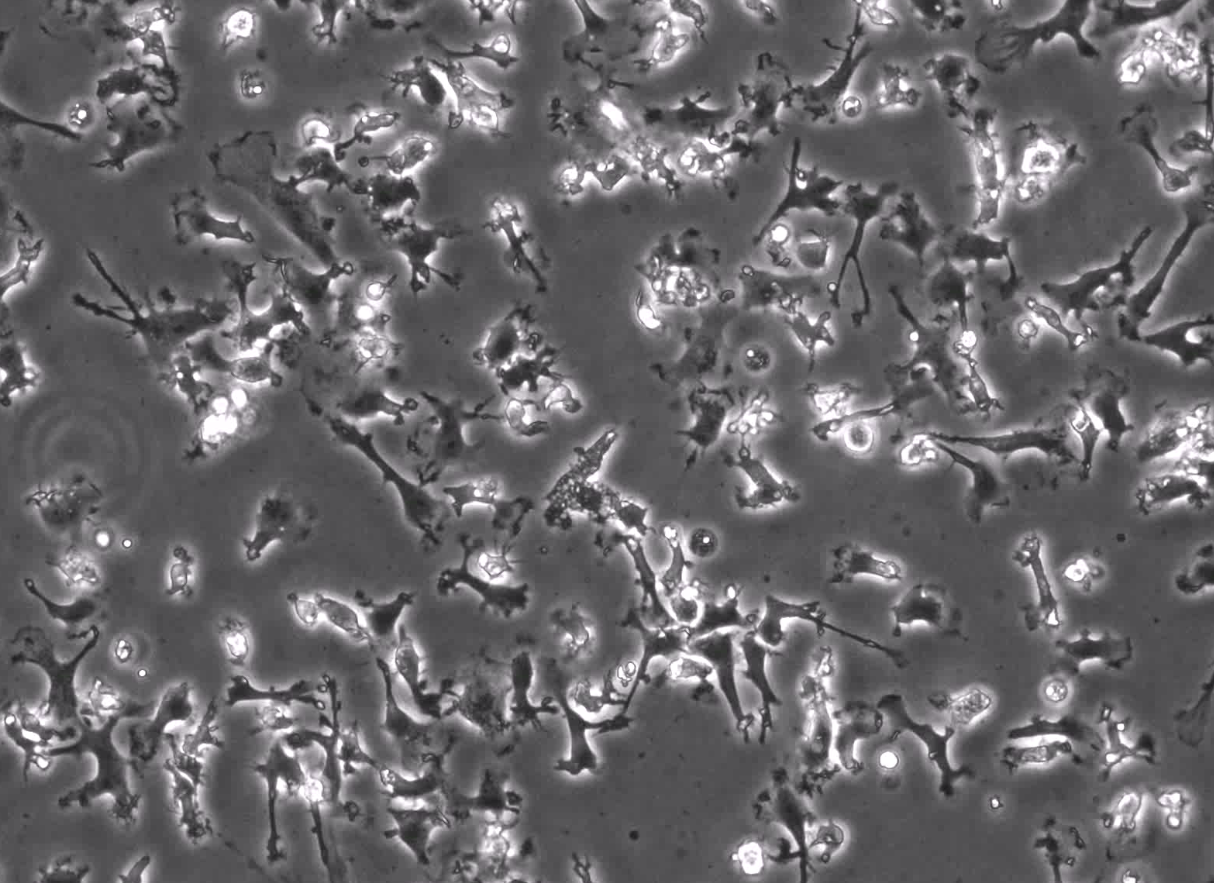
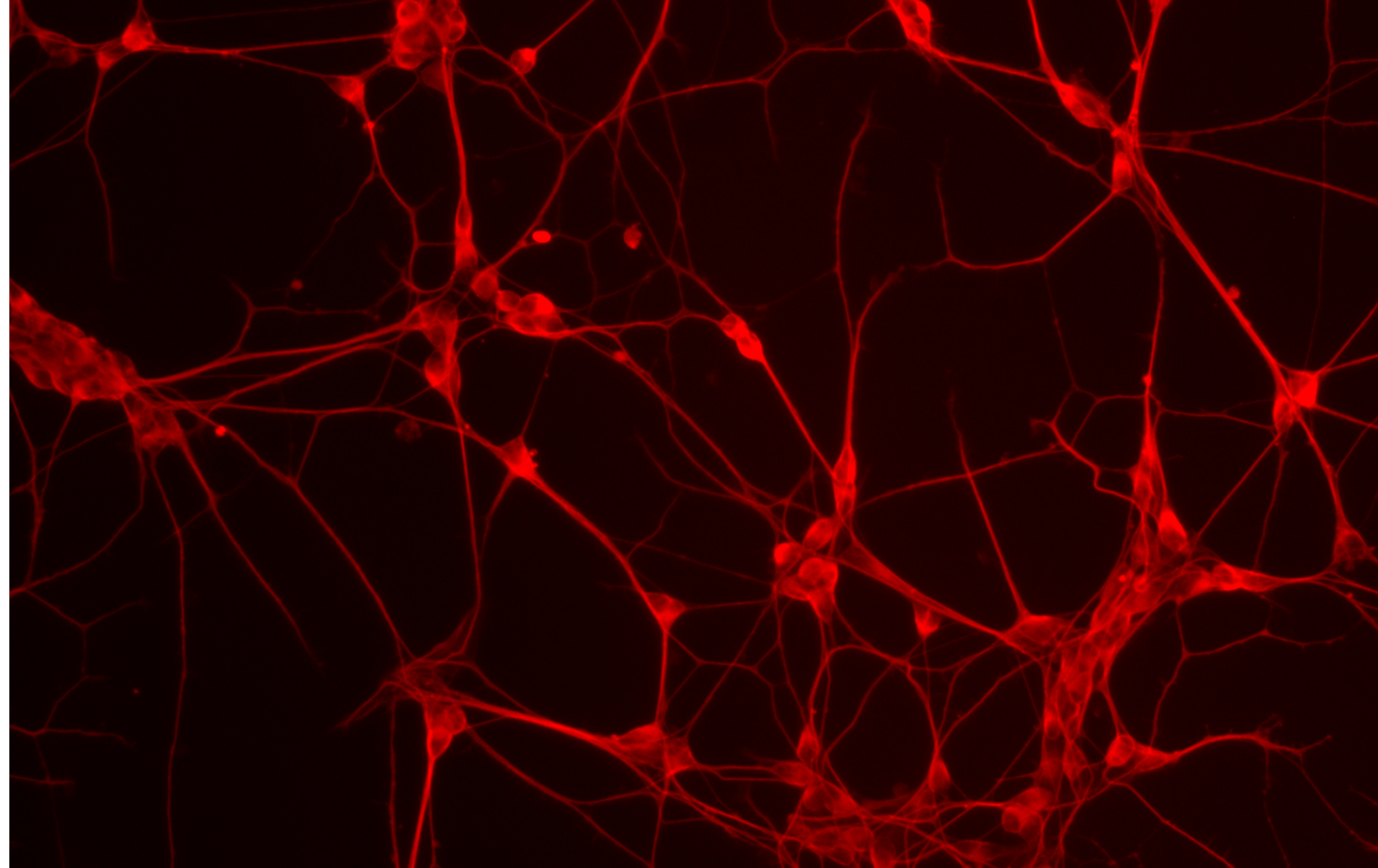
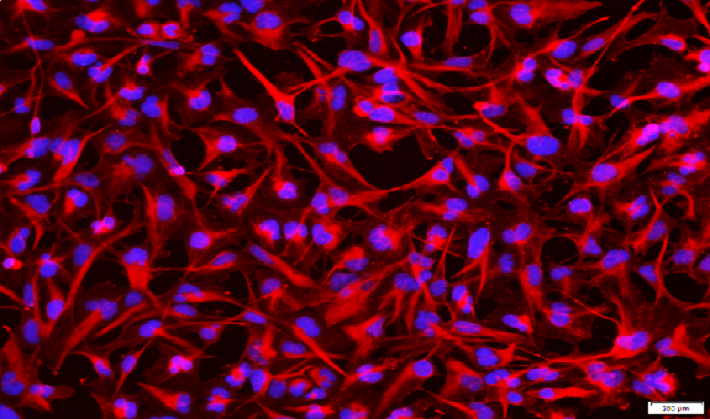
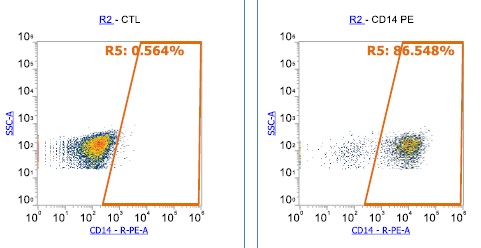
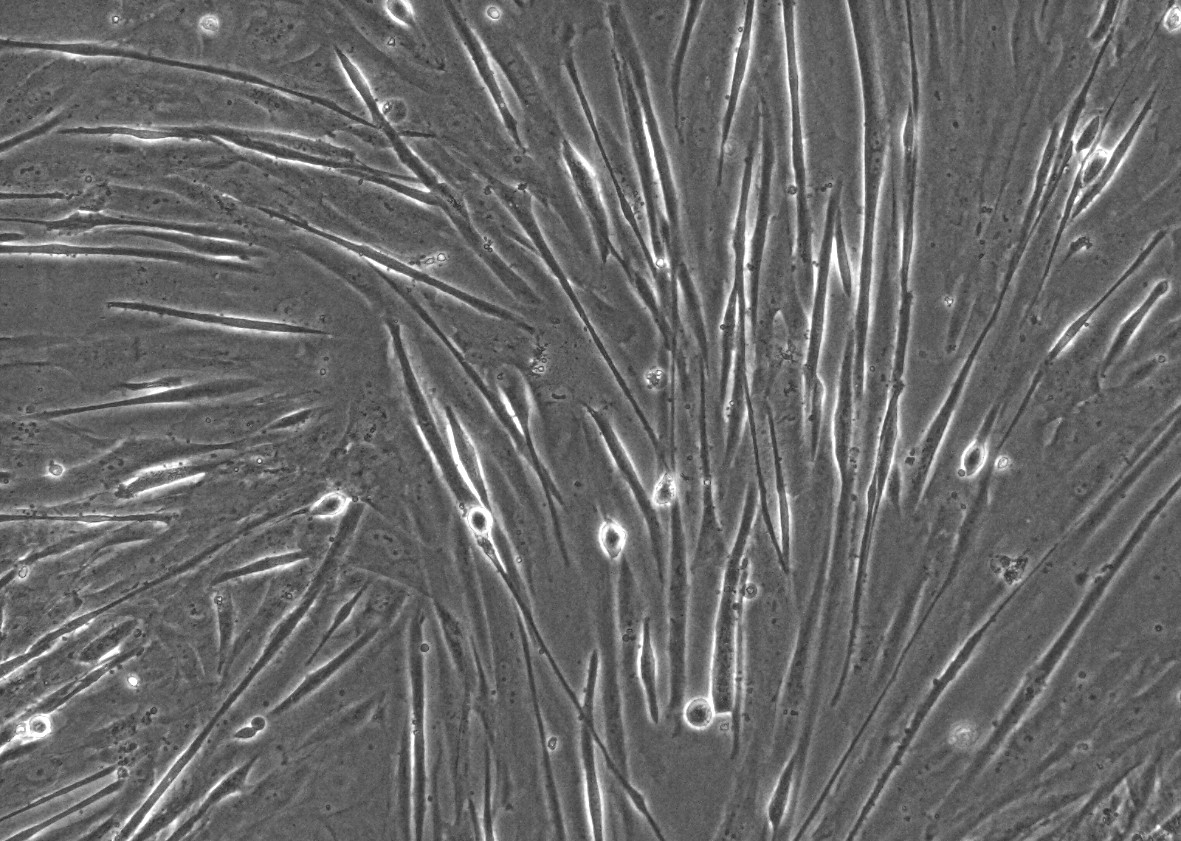
iPSC-derived Cells
induced Pluripotent Stem Cells (iPSCs)
Induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) are a type of stem cell that are generated from adult cells, such as skin cells or blood cells, through a process called reprogramming. iPSCs possess the remarkable ability to differentiate into various cell types found in the body, including neurons, cardiomyocytes, hepatocytes, and more. These differentiated cells, derived from iPSCs, are referred to as iPSC-derived cells.
iPSC-derived cells have significant potential in biomedical research and regenerative medicine
iPSC-derived cells are of great interest in research due to their ability to model human biology, providing a versatile platform for:
- Disease Modeling: iPSC-derived cells can be generated from individuals with specific genetic disorders or diseases, allowing researchers to model disease processes in vitro. By studying how these cells behave in culture, scientists can gain insights into disease mechanisms, identify therapeutic targets, and screen potential drugs for efficacy.
- Drug Discovery and Toxicity Testing: iPSC-derived cells provide a platform for screening potential drug candidates and assessing their safety and efficacy. These cells can be used to evaluate drug responses in a more physiologically relevant context, potentially reducing the reliance on animal models and improving the predictability of preclinical studies.
- Cell Replacement Therapy: iPSC-derived cells hold promise for cell replacement therapies aimed at treating a wide range of diseases and injuries. For example, iPSC-derived cardiomyocytes could be used to repair damaged heart tissue in patients with heart disease, while iPSC-derived neurons could be transplanted to restore function in individuals with neurodegenerative disorders like Parkinson’s disease.
- Personalized Medicine: iPSC technology enables the generation of patient-specific cells, allowing for personalized approaches to treatment and drug development. By creating iPSC-derived cells from individuals with specific genetic backgrounds or disease phenotypes, clinicians can tailor therapies to the unique needs of each patient.
- Basic Research: iPSC-derived cells serve as valuable tools for studying basic biological processes, such as development, differentiation, and cell signaling. These cells provide a renewable and scalable source of human cells for experimentation, enabling researchers to address fundamental questions in biology and medicine.
Overall, iPSC-derived cells have revolutionized the field of regenerative medicine and biomedical research, offering new opportunities for understanding disease mechanisms, developing novel therapies, and advancing personalized medicine approaches.
-
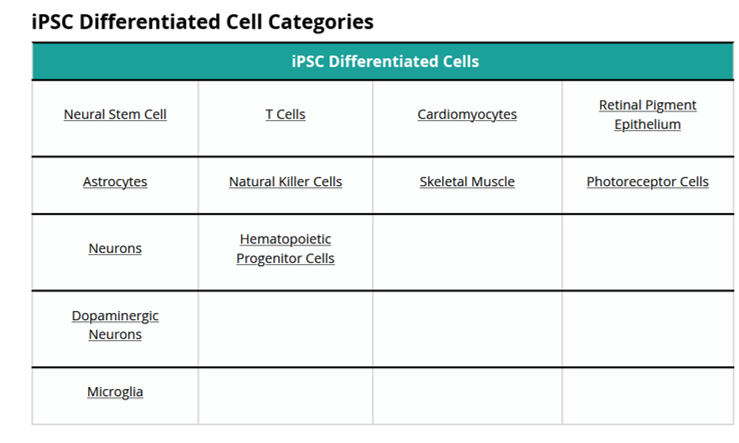
iPSC Differentiated Cells - Overview
Cat.-Nr: ASC-0001C
Take advantage of 25% off on these iPSC-derived Cells with Media – offer ends December 31, 2025 High-Quality iPSC-Derived Cells with Media for... Read More
-
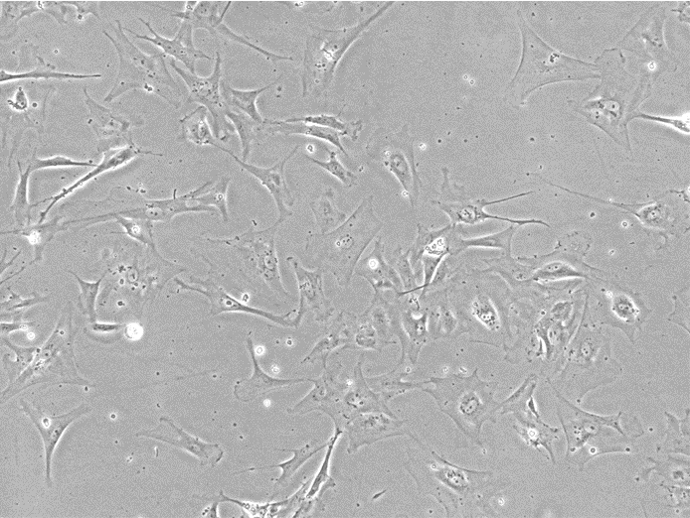
iPSC-derived Astrocytes with Medium
Cat.-Nr: ASE-9743
Take advantage of 25% off on these iPSC-derived Cells with Media – offer ends December 31, 2025 iPSC-derived Astrocytes with... Read More
-
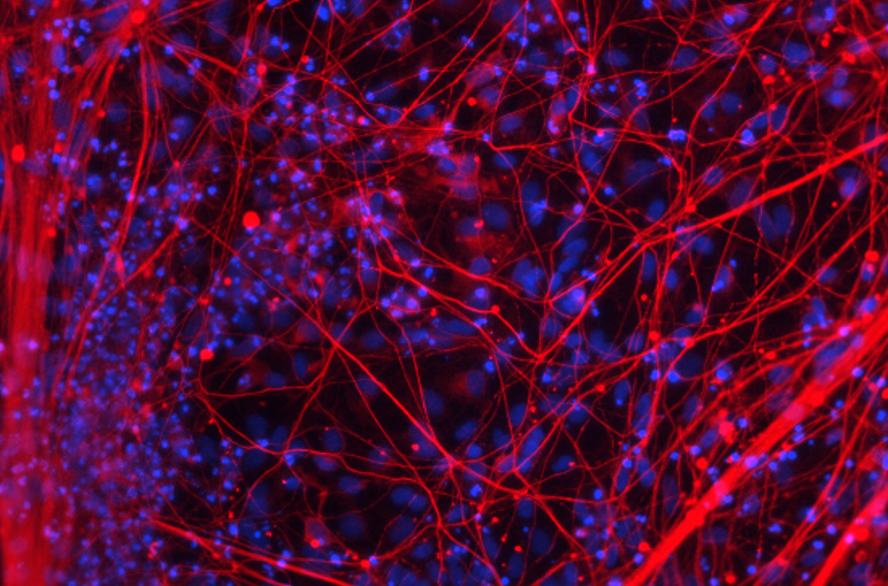
iPSC-derived Cortical Neurons with Media
Cat.-Nr: ASE-9741
Take advantage of 25% off on these iPSC-derived Cells with Media – offer ends December 31, 2025 Applied StemCell has developed an efficient... Read More
-
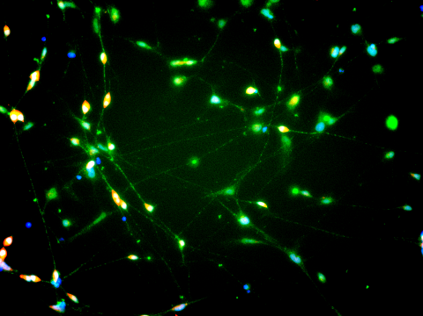
iPSC-derived Dopaminergic Neurons with Media
Cat.-Nr: ASE-9742
Take advantage of 25% off on these iPSC-derived Cells with Media – offer ends December 31, 2025 iPSC-derived Dopaminergic Neurons with... Read More
-
iPSC-derived Endothelial Cells with Media
Cat.-Nr: ASE-9744
Take advantage of 25% off on these iPSC-derived Cells with Media – offer ends December 31, 2025 Applied StemCell has developed an... Read More
-
iPSC-derived Human Cardiomyocytes with Media
Cat.-Nr: ASE-9703
Take advantage of 25% off on these iPSC-derived Cells with Media – offer ends December 31, 2025 Applied StemCell has developed an efficient... Read More
-
iPSC-Derived Human Hematopoietic Progenitor Cells with Media
Cat.-Nr: ASE-9718
Take advantage of 25% off on these iPSC-derived Cells with Media – offer ends December 31, 2025 Applied StemCell has developed an... Read More
-
iPSC-derived Human Microglia (iMGLs) with Media
Cat.-Nr: ASE-9601
Take advantage of 25% off on these iPSC-derived Cells with Media – offer ends December 31, 2025 Microglia are the primary immune cells in the... Read More
-
iPSC-derived Human Motor Neurons with Media
Cat.-Nr: ASE-9701
Take advantage of 25% off on these iPSC-derived Cells with Media – offer ends December 31, 2025 Motor neurons (MN) are specialized neurons... Read More
-
iPSC-derived Human Neural Progenitor Cells with Media
Cat.-Nr: ASE-9740
Take advantage of 25% off on these iPSC-derived Cells with Media – offer ends December 31, 2025 Applied StemCell has developed an efficient... Read More
-
iPSC-derived Human Neural Stem Cells (NSC)
Cat.-Nr: IC-0001
iPSC-derived Human Neural Stem Cells, Male, provide an ideal culture model for the study of multipotent stem cell biology. Induced Pluripotent... Read More
-
iPSC-derived Monocytes with Media
Cat.-Nr: ASE-9745
Take advantage of 25% off on these iPSC-derived Cells with Media – offer ends December 31, 2025 Applied StemCell has developed... Read More
-
iPSC-derived Myoblasts with Media
Cat.-Nr: ASE-9706
Take advantage of 25% off on these iPSC-derived Cells with Media – offer ends December 31, 2025 Applied StemCell has developed an... Read More
-
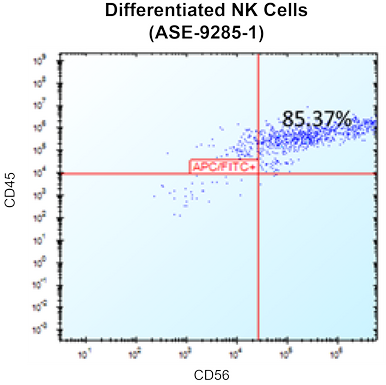
iPSC-Derived Natural Killer (NK) Cells with Media
Cat.-Nr: ASE-9285
Take advantage of 25% off on these iPSC-derived Cells with Media – offer ends December 31, 2025 Applied StemCell has developed an... Read More
-
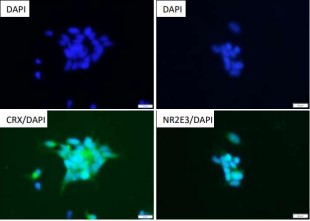
iPSC-derived Photoreceptor Progenitor Cells with Media
Cat.-Nr: ASE-9715
Take advantage of 25% off on these iPSC-derived Cells with Media – offer ends December 31, 2025 Applied StemCell has developed an efficient... Read More
-
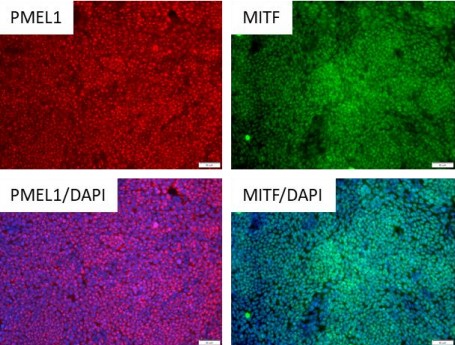
iPSC-derived Retinal Pigment Epithelium (RPE) Cells with Media
Cat.-Nr: ASE-9710
Take advantage of 25% off on these iPSC-derived Cells with Media – offer ends December 31, 2025 Applied StemCell has developed an efficient... Read More
-
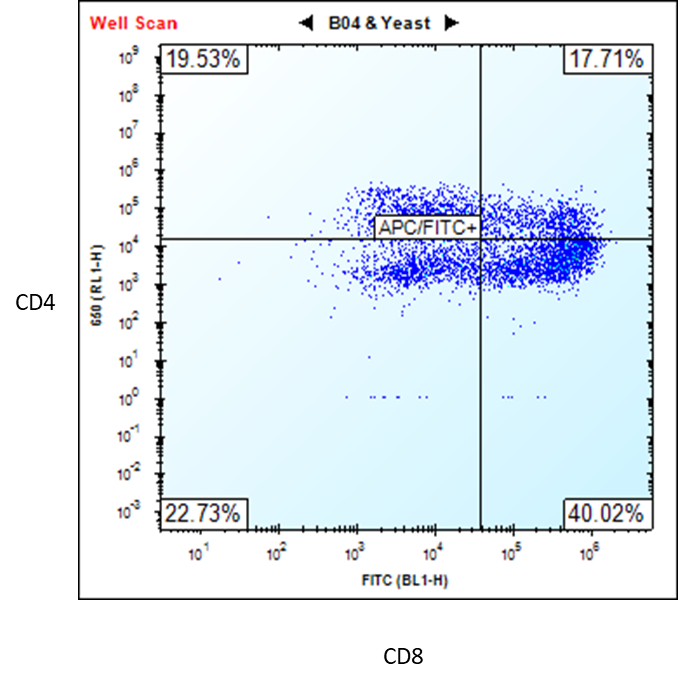
iPSC-derived T Cells with Media
Cat.-Nr: ASE-9720
Take advantage of 25% off on these iPSC-derived Cells with Media – offer ends December 31, 2025 Applied StemCell has developed an... Read More